Data Products: Clear Sky Mask
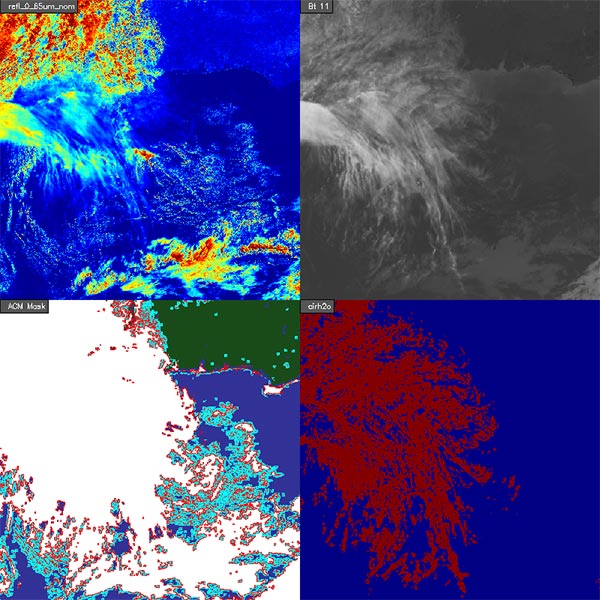
The clear sky mask algorithm takes advantage of the high spatial and temporal resolution of the GOES-R ABI visible, near-infrared, and infrared bands to automatically produce a cloud classification for each pixel: cloudy, probably cloudy, clear, or probably clear. This information is used extensively by downstream level-2 product algorithms that require the state of cloudiness in each pixel. Products such as land surface temperature (LST) and sea surface temperature (SST), for example, can only be reliably computed for pixels that are totally cloud free. The clear sky mask product can be used by the numerical weather prediction (NWP) community to identify which ABI pixel information should be assimilated for use in NWP models.