GOES-R Series News | 2023
-
December 8, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Atmospheric Rivers Drench the Pacific Northwest
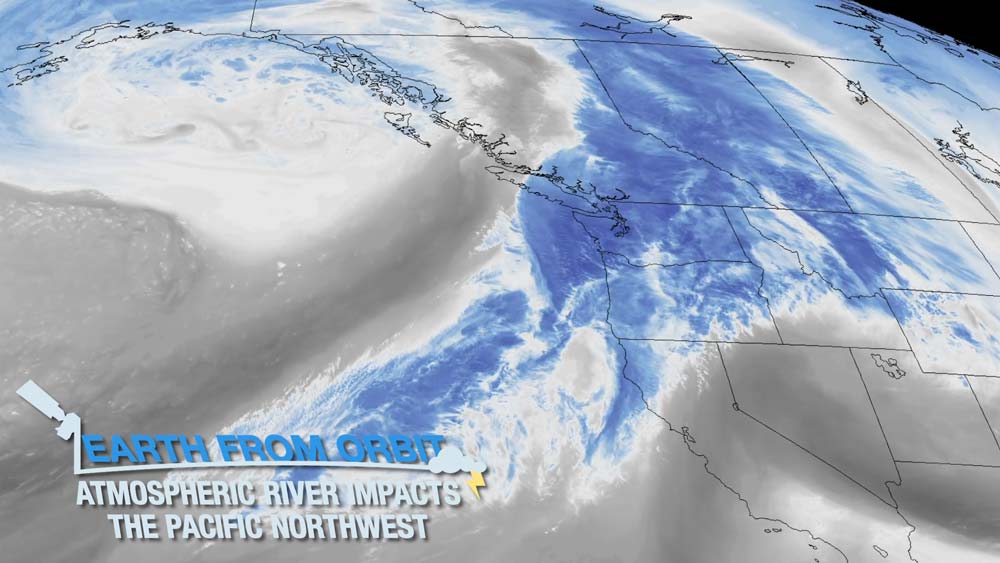
NOAA satellites monitored a series of storms from an atmospheric river that impacted the Pacific Northwest in early December 2023. On Dec. 4, the storms brought record-breaking rainfall, flooding, and significant snowfall to some areas. Atmospheric rivers are long, narrow belts of moisture that move through the atmosphere. GOES-18 (GOES West) tracked the band of moisture as it moved over the Pacific Ocean and into the Pacific Northwest in near real-time. NOAA satellites provide critical data for forecasting atmospheric weather river events and monitoring the weather conditions they bring.
December
-
November 28, 2023: Earth from Orbit: 2023 Atlantic Hurricane Season Wraps Up

NOAA satellites constantly monitor the ocean for tropical activity. As the 2023 Atlantic hurricane season comes to a close, we’re looking back at this above-normal season. This season was very active in terms of the number of named storms, ranking fourth for most named storms in a year. The Atlantic basin saw 20 named storms in 2023. Seven of these were hurricanes and three intensified to major hurricanes (Category 3 or higher on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale). An average season has 14 named storms, seven hurricanes and three major hurricanes. Although the season runs from June 1 to Nov. 30, tropical and subtropical cyclone formation can occur at any time and NOAA satellites will be keeping watch.
-
November 02, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Hurricane Otis Causes Catastrophic Damage
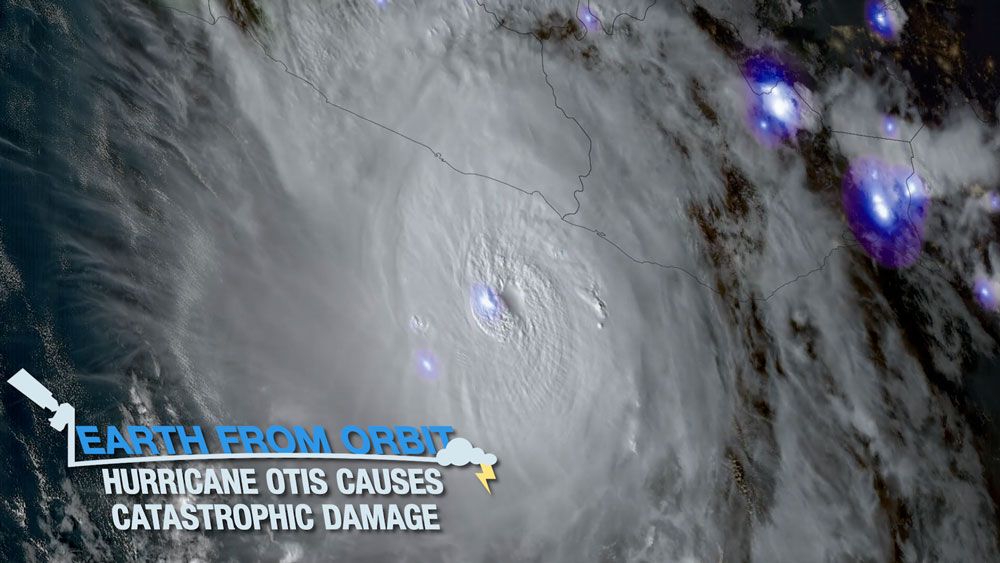
On Oct. 25, 2023, NOAA satellites monitored Hurricane Otis as it hit Mexico’s southern Pacific coast near Acapulco as a Category 5 storm. Otis was the strongest hurricane in the Eastern Pacific to make landfall in the satellite era. The hurricane brought storm surge, flooding, mudslides, and strong winds to the coast and caused widespread damage and fatalities in the region. GOES East and GOES West watched in near real-time as Otis rapidly intensified from a tropical storm to a Category 5 hurricane within a 24-hour period. The Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM) measured lightning within the eyewall while it was rapidly intensifying. Infrared imagery showed the structure of the storm as it developed and intensified before making landfall.
November
-
October 19, 2023: Earth from Orbit: NOAA Satellites View Annular Eclipse
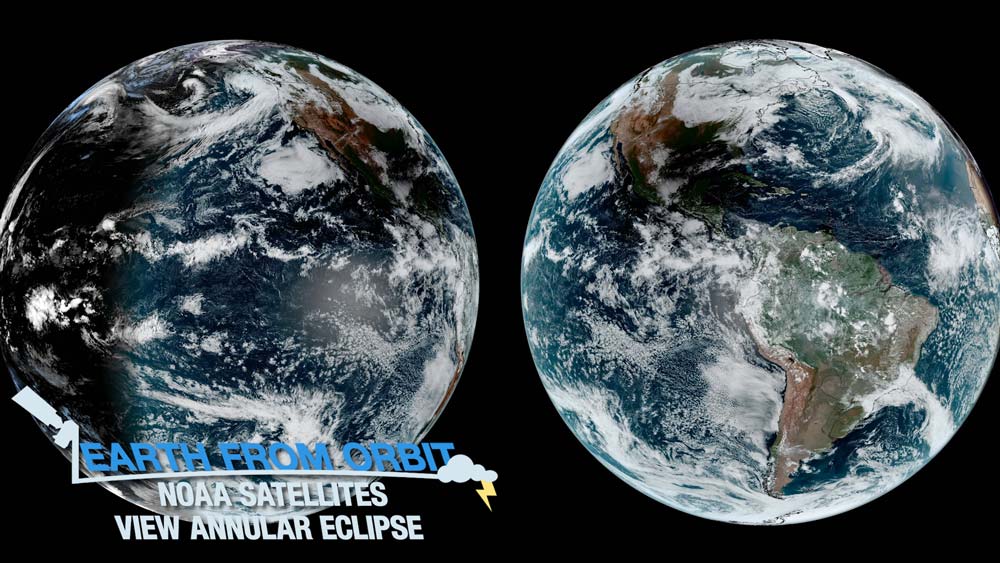

On Oct. 14, NOAA satellites caught an annular eclipse as it traversed parts of North, Central, and South America. A solar eclipse occurs when the moon crosses between the Earth and the sun, and casts a shadow. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the moon is farther away from Earth when they pass each other. In this event, the moon does not completely block out the sun and causes a ring of fire to appear. NOAA’s GOES satellites viewed the moon’s shadow as it moved across the Earth in near real-time. The Solar Ultraviolet Imager (SUVI) onboard GOES East also captured the eclipse. SUVI observed the moon crossing in front of the sun. As the April 8, 2024 total solar eclipse approaches, NOAA satellites will be waiting to capture the event.
-
October 12, 2023: Third Quarter 2023 GOES-R/GeoXO Newsletter

GeoXO Imager System Requirements Review/System Definition Review participants. Photo credit: L3Harris The GOES-R/GeoXO quarterly newsletter for July – September 2023 is now available. The GOES-R and GeoXO programs accomplished a lot this quarter. GOES-U completed environmental testing and is preparing for its Pre-Shipment Review at the end of October. The ground, flight, and mission operations teams are busy conducting rehearsals and readiness exercises to prepare for the April 2024 launch. We awarded the second GeoXO development contract to build the Sounder and released three development RFPs this quarter – for the Lightning Mapper and Ocean Color instruments and the spacecraft. Also, the GeoXO Imager had a successful System Requirements Review/System Definition Review and is proceeding to the preliminary design phase. And we welcomed our new deputy program director, Brian Hall.
-
October 06, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Heavy Rains Cause Flooding in New York City

The remnants of Tropical Storm Ophelia over the Atlantic Ocean combined with a mid-latitude system arriving from the west unleashed more than eight inches of rain in parts of the New York metropolitan area on Sept. 28-29, 2023. NOAA satellites monitored conditions as torrential rain led to flood water coursing through streets and into basements, schools, subways, and vehicles throughout the nation’s most populous city. Data from GOES and JPSS were also used to produce flood maps that helped to determine the impact of the storm – where flooding was happening, what the extent was, how long it would last, and what damage occurred.
October
-
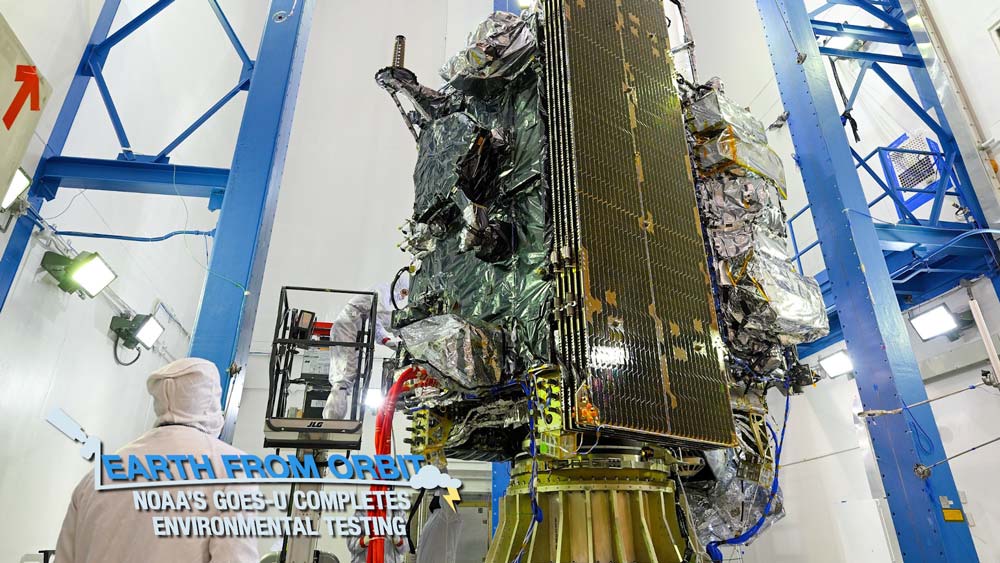
September 14, 2023: NOAA’s GOES-U Completes Environmental Testing

GOES-U, the fourth and final satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series of advanced geostationary satellites, recently completed rigorous testing to ensure it can withstand the harsh conditions of launch and maintain functionality in orbit 22,236 miles above Earth. The testing process spanned nearly a year and was conducted by Lockheed Martin and SpaceX personnel at the Lockheed Martin facility in Littleton, Colorado, where the satellite was built. GOES-U is on track for an April 2024 launch from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida aboard a Falcon Heavy launch vehicle.
September
-
August 24, 2023: Earth from Orbit: 2023 Hurricane Activity Ramps Up

NOAA satellites have been monitoring increased tropical activity in the Atlantic and Pacific, with five named storms developing in the last week. As NOAA satellites were monitoring Tropical Storm Hilary as it brought torrential rainfall, flooding, and mudslides to Southern California, a series of storms were forming in the Atlantic. Within the span of 18 hours, three tropical storms formed—Emily, Franklin, and Gert. While Emily and Gert were relatively short-lived and dissipated over the ocean, Franklin, which formed east of the Leeward Islands, made landfall in the Dominican Republic on August 23, bringing heavy rains to Hispaniola. By August 22, another tropical storm, Harold, formed in the western Gulf of Mexico, making it the fourth Atlantic named storm to form within 39 hours. Harold made landfall on San Padre Island, Texas on August 22, and was the first Atlantic storm this season to do so in the U.S. August 20 marked the beginning of what is typically the most active portion of the Atlantic hurricane season. Historically, more than 85 percent of all major (Category 3, 4, and 5) Atlantic hurricanes form after this date. As the Atlantic and Pacific hurricane seasons continue, NOAA satellites remain our watchful eyes in the sky, providing critical information for hurricane forecasting, tracking, and intensity estimation.
-
August 11, 2023: NOAA Releases Updated 2023 Atlantic Hurricane Season Outlook

On Aug. 10, NOAA updated its 2023 Atlantic hurricane season outlook. NOAA is now expecting above normal activity in the Atlantic. El Niño and record sea surface temperatures are contributing factors. The update includes an increase in named storms to 14-21, with 6-11 developing into hurricanes. Of those, 2-5 are anticipated to be major hurricanes – Category 3 or higher. The 2023 Atlantic hurricane season started early on Jan. 16 with an unnamed subtropical storm that formed southeast of Nantucket, Massachusetts. Since the first official day of the 2023 Atlantic hurricane season, June 1, there have been four named storms: Arlene, Bret, Cindy and Don. Out of the four, only one strengthened into a hurricane. Hurricane Don developed into a Category 1 hurricane on July 22 in the northern Atlantic. NOAA satellites provide critical data for hurricane forecasting as well as advanced technology to track the storms—their location, movement, and intensity. The satellites provide a detailed look at storm properties, specific features of a hurricane’s eye, wind estimates, and lightning activity. As peak hurricane season approaches, NOAA satellites will be watching for the development of these storms.
August
-
July 28, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Fires Blaze Across Western U.S.

As record-breaking heat continues to scorch parts of the southwestern U.S. and Mexico, NOAA satellites are monitoring fires in the western U.S., which are sending plumes of smoke into the atmosphere. As of July 26, 2023, a total of 39 fires have burned 201,637 acres in nine states, including Arizona, New Mexico, Oregon, Idaho, Colorado, California, Texas, Montana, and Washington. NOAA satellites are tracking the fires and their impact. GOES-18 (GOES West) identified hot spots as they ignited and monitored the movement of smoke from the fires in near real-time. GOES-18 also helped determine fire size and temperature.
-
July 21, 2023: Earth from Orbit: NOAA Satellites Monitor Severe Weather and Smoke

As catastrophic flooding impacted the Northeast, skies across the region and particularly along the central and eastern U.S. have also been affected by heavy smoke from wildfires burning across Canada that has continued to drift southward. NOAA satellites monitored conditions as the events unfolded. GOES-16 measured water vapor that was transported in the atmosphere, and monitored the storms that drenched the Northeast in near real-time. GOES-16 and 18 tracked the intense smoke from Canadian wildfires as it moved into the central and eastern U.S., triggering air quality alerts. From fires to floods, NOAA satellites help warn us of approaching hazards.
-
July 13, 2023: Second Quarter 2023 GOES-R/GeoXO Newsletter

Geostationary Ground Services Sustainment team celebrates the award of the sustainment contract. Photo credit: GOES-R The GOES-R/GeoXO quarterly newsletter for April – June 2023 is now available. It was, as ever, a busy quarter for us. The GOES-R ground system server replacement effort concluded and we awarded the follow-on ground sustainment contract. We continued environmental testing of the GOES-U satellite and the mission integration efforts with the Falcon Heavy launch vehicle. On the GeoXO front, work on the imager development contract began and we finished the remaining Phase A Studies. The departures of 30+ year GOES alumni John Fiorello and our longtime DPM Ed Grigsby, and the sadly too-soon passing of our Review Manager Jonathan Gal-Edd are reminders to value and enjoy the colleagues and friends we make along the way.
July
-
June 30, 2023: Extreme Heat and Severe Weather Plague Parts of North America
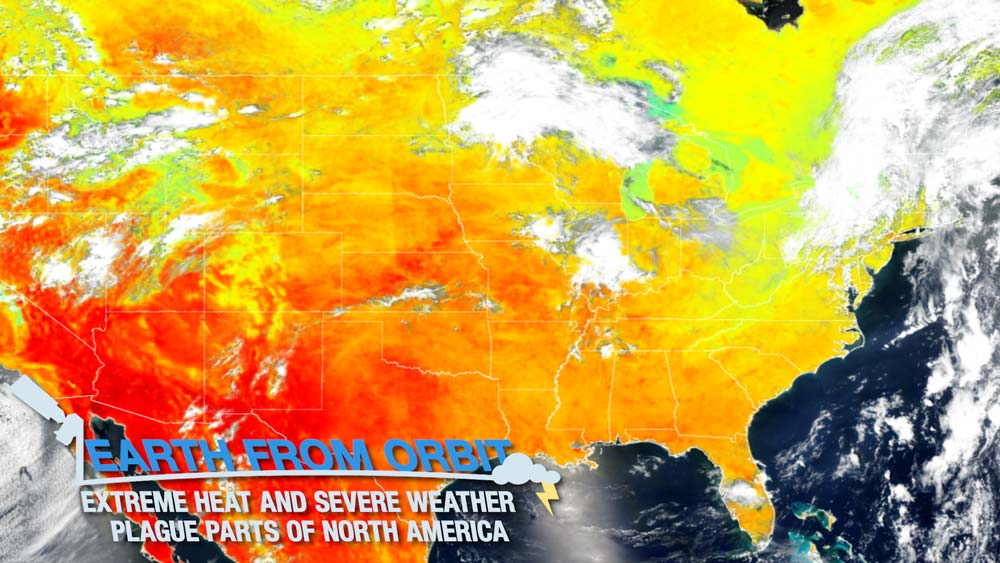
NOAA satellites have been watching the effects of a heat dome that settled over Texas and parts of Mexico since early June 2023. The heat dome is expected to spread northward and persist through July 4 with no relief in sight. A heat dome is a ridge of high pressure that traps hot air. While the heat dome is causing record-breaking temperatures in the south, it has also led to severe weather. The edge of the heat dome meeting with cooler air can trigger severe thunderstorms, tornados, and high winds. The NOAA/NASA Suomi NPP and NOAA-20 satellites measured land surface temperature, revealing the extent of the heat dome. Data collected by the satellites is used within models such as the Global Forecast System to accurately predict conditions. Meanwhile, GOES East watched the heat dome interact with cooler air in near real-time as is seen with water vapor imagery. As these explosive storms developed along the edge of the dome and traveled eastward, GOES tracked their movement. GOES East also measured lightning within the storms and infrared imagery from the satellite revealed the intensity of the storms.
-
June 21, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Summer Solstice 2023

June 21, 2023, marks the start of astronomical summer in the Northern Hemisphere. The summer solstice is the moment the hemisphere reaches its greatest tilt toward the sun. NOAA’s GOES-16 and -18 satellites constantly observe the same region of Earth, allowing a view of the terminator as it moves across the Western Hemisphere. The terminator is the edge between the shadows of nightfall and the sunlight of dusk and dawn. The slope of the terminator curve changes with the seasons. The summer solstice is the longest day, and shortest night, of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
-
June 20, 2023: NOAA Satellites Tracked Historic Levels of Harmful Smoke, Impacting Millions in the Eastern U.S.
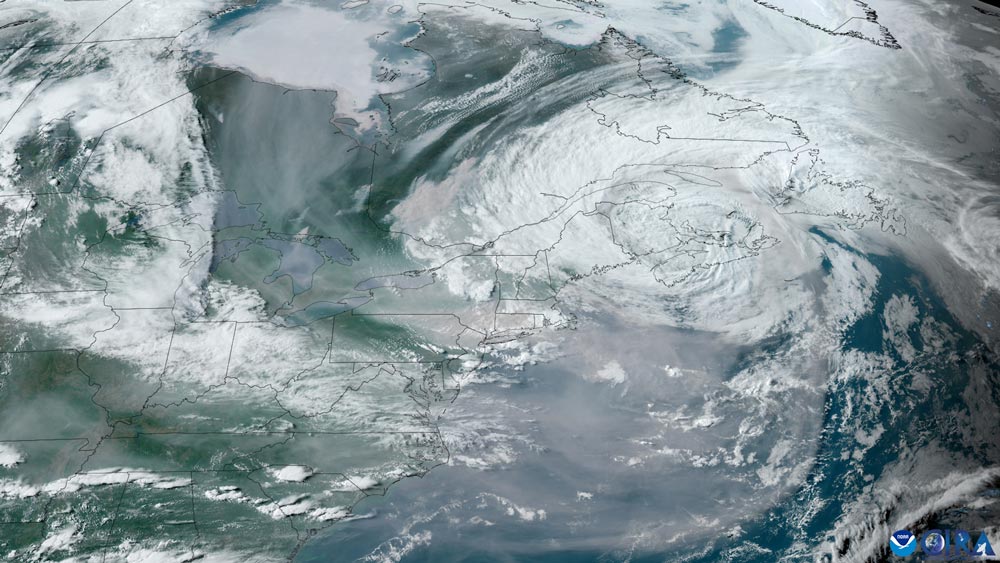
GOES-16 imagery from June 6, 2023, shows a coastal low-pressure system steering heavy smoke across the Northeast and Mid-Atlantic United States. NOAA satellites, including GOES-16, provided critical data for air quality forecasters when wildfires, burning near Quebec, Canada, sent billowing plumes of smoke over the eastern United States. The satellite data allowed NOAA scientists to estimate that more than 86 million people experienced fine particulate pollution levels higher than the federal health standard. During the early-June episode, NOAA satellite observations of the smoke helped forecasters issue air quality alerts to protect public health. GOES data of fine particulate pollution are increasingly being used in nowcasting mode to provide warnings to the public.
-
June 20, 2023: Lightning Detection: From Ground to Sky
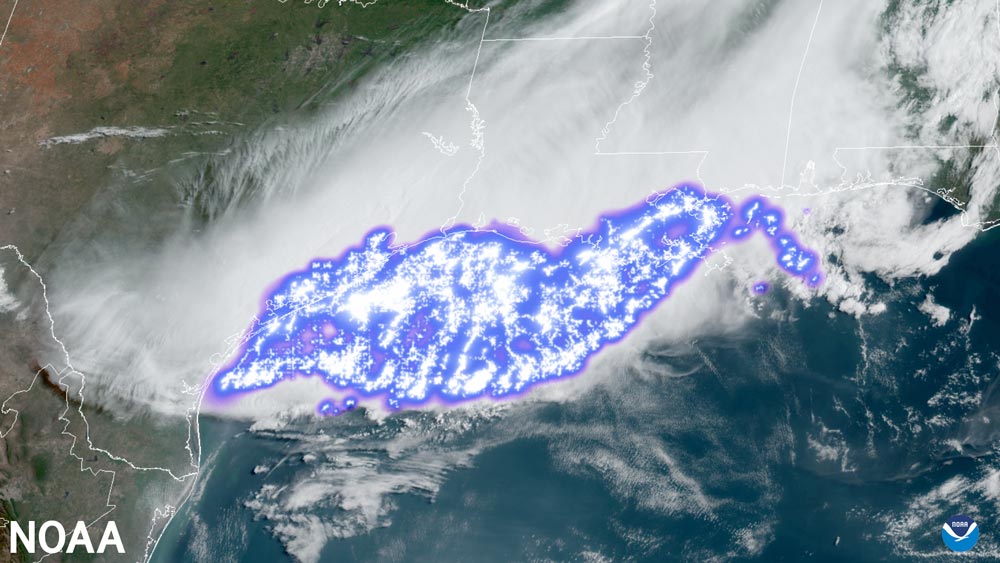
GOES-16 GLM image from April 20, 2020, of the longest lightning flash on record, which covered a horizontal distance of 477 miles. Lightning may be stunning, but it is also a deadly, destructive force. Meteorologists have studied lightning for centuries, working out its behavior and developing ways to detect lightning strikes. Tools and techniques for lightning detection have come a long way since Benjamin Franklin tested his lightning rod, shifting our view of this powerful severe weather from the ground to the sky. Satellites have allowed us to detect and map lightning storms like never before – from space. The GOES-R Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM) is the first optical lightning detector on a satellite in geostationary orbit. NOAA began using the GLM in March 2017. In July 2018, the National Weather Service started including its data in the determination of operational weather forecasts.
-
June 12, 2023: WeatherSats Augmented Reality App

Learn about the JPSS and GOES-R satellites that monitor extreme weather and climate change in the new WeatherSats immersive AR app. It challenges you to complete a series of missions, which will start with an interactive journey into space where you’ll see the satellites orbiting Earth and view all of their instruments up close. Play at home or play the app's six challenges at the NASA Goddard Visitor Center! Available for download to your mobile device from the Apple and Google app stores.
-
June 8, 2023: Smoke From Canadian Wildfires Blankets U.S.

More than 400 fires are burning across Canada, blanketing regions throughout North America with thick smoke. NOAA satellites are monitoring the smoke as it drifts across the continent. Unusually hot and dry weather triggered an early and intense start to the wildfire season in Canada and the country is on track to have the worst wildfire season on record. Recently, smoke from fires in Ontario and Quebec moved into the eastern U.S., triggering air quality alerts across the region. According to NOAA’s Aerosol Watch, the smoke caused a historic Code Red (unhealthy) daily Air Quality alert of 2.5 parts per million across New York, eastern Pennsylvania, and western Connecticut on June 6, 2023. There was even a Code Purple (very unhealthy) in some parts of New York City and Philadelphia. As of the morning of June 7, historically high fine particulate concentrations were seen further south into the Mid-Atlantic region, and reports from the ground stated limited visibility and campfire-like smells. GOES East and GOES West are tracking the billowing smoke and monitoring air quality in near real-time. JPSS satellites are collecting data to help determine the height of the smoke plume, the amount of smoke produced, and the direction it’s expected to move. Together, NOAA satellites provide critical information for detecting and tracking fires and alerting communities to poor air quality from smoke produced by the blazes.
-
June 2, 2023: Can Lightning Research Improve Hurricane Intensity Forecasts? A Q&A With NOAA's Dr. Stephanie Stevenson

Dr. Stephanie Stevenson Dr. Stephanie Stevenson is a meteorologist at the NOAA/National Weather Service National Hurricane Center (NHC) in Miami. Through her ground-breaking research and efforts, new applications using GOES-R Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM) data are being used as guidance for NHC forecasts as well as in media and decision-support briefings. With 2023’s Atlantic Hurricane Season officially underway, NESDIS recently interviewed Dr. Stevenson to learn more about her research and what it means for the future of hurricane tracking and forecasting.
June
-
May 31, 2023: Time-lapse of Solar Cycle 25 Displays Increasing Activity on the Sun
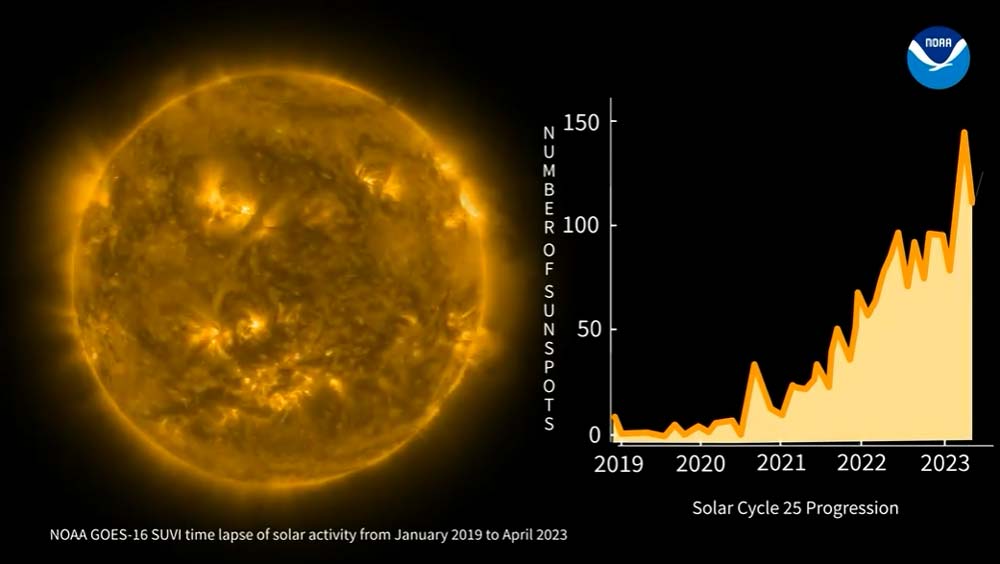
GOES-16 SUVI imagery alongside the progression of the number of sunspots from December 2019 through April 2023. Solar Cycle 25 has ramped up much faster than scientists predicted producing more sunspots and eruptions than experts had forecast. Tracking and predicting the sun’s solar cycles gives a rough idea of the frequency of space weather storms of all types – from radio blackouts to geomagnetic storms and solar radiation storms – and it’s used by many industries to gauge the potential impact of space weather on Earth. A new time lapse animation shows GOES-16 Solar Ultraviolet Imagery (SUVI) during Solar Cycle 25 from December 2019 through April 2023 alongside the progression of the number of sunspots. SUVI images the solar corona in six different extreme ultraviolet wavelengths. NOAA’s space weather forecasters use SUVI imagery to issue alerts and watches for space weather storms.
-
May 31, 2023: 2023 GOES Virtual Science Fair Top Projects Announced
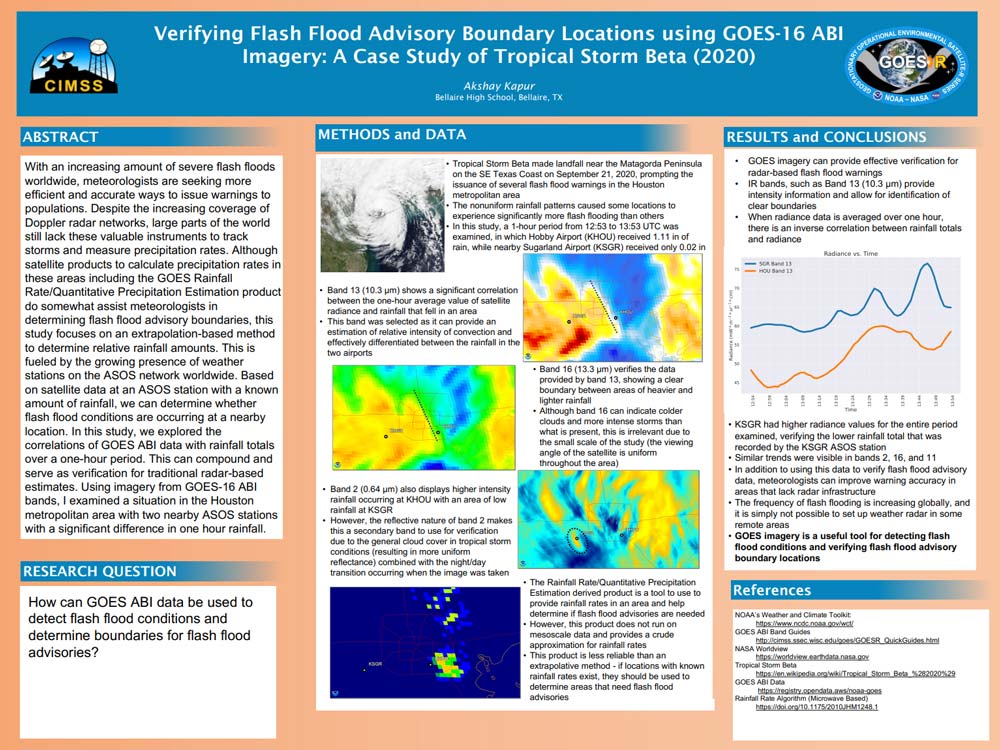
2023 top GOES high school project: Verifying Flash Flood Advisory Boundary Locations using GOES-16 ABI Imagery: A Case Study of Tropical Storm Beta (2020) The Cooperative Institute of Meteorological Satellite Studies at the University of Wisconsin-Madison announced the winning projects for the 2023 GOES Virtual Science Fair. During the virtual science fair, middle and high school students (grades 6-12) worked with GOES satellite data to investigate weather and natural hazards and conveyed their projects with scientific posters. High school submissions also required a short video where students explain their project, similar to a poster session at a professional conference. By offering authentic STEM (science, technology, engineering and math) engagement to a pre-college audience, this activity serves as a pipeline to society’s scientists of tomorrow and NOAA’s future workforce
-
May 25, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Popocatépetl Volcano Erupts in Mexico
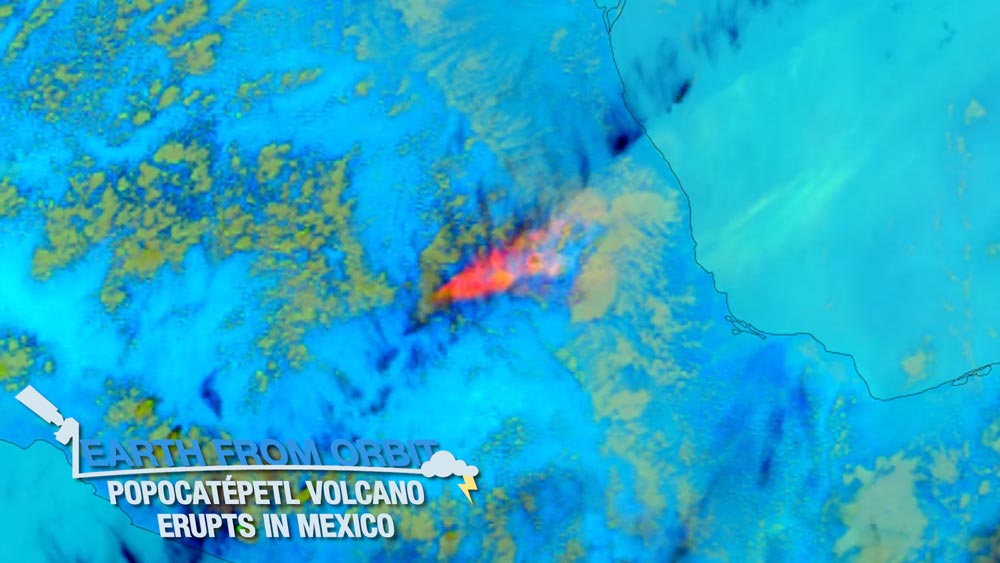
Since May 15, 2023, NOAA satellites have been watching Mexico’s Popocatépetl Volcano exhibit activity ranging from tremors to spewing ash. Popocatépetl, Aztec for smoking mountain, is located 45 miles southeast of Mexico City. With about 25 million people living within 60 miles of Popocatépetl, it is considered one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the world. Geostationary satellites, like GOES-16 and GOES-18, are the primary tool for monitoring volcanic clouds. GOES-16 observed Popocatépetl’s ash plumes in near real-time and monitored hazardous sulfur dioxide from the volcano. JPSS satellites measured smoke, ash and dust from the volcano. Together, NOAA satellites help monitor volcanoes and the risks they pose.
-
May 11, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Wildfires Rage in Western Canada
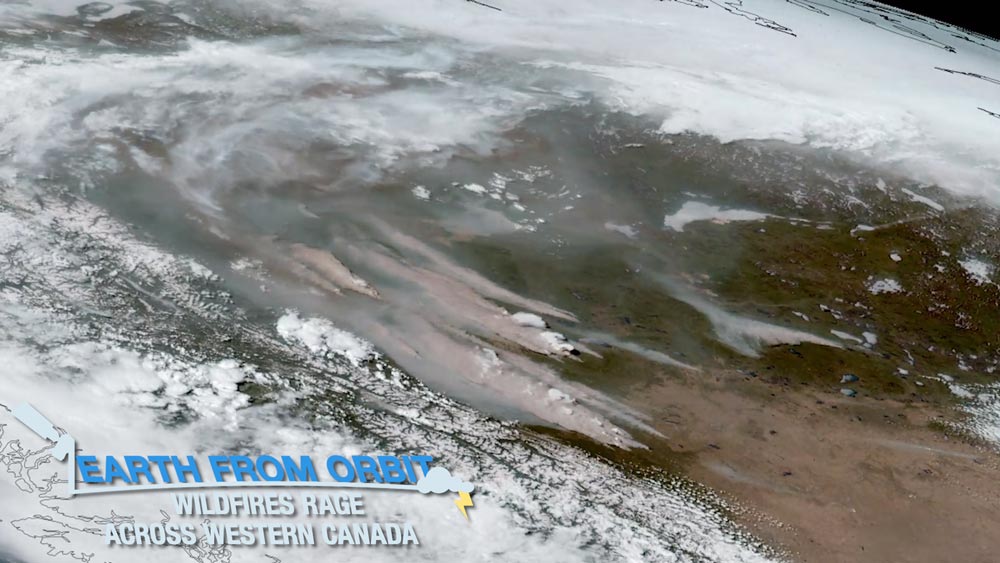

In early May 2023, fires ignited across western Canada due to unusually hot and dry weather. NOAA satellites watched as the fires raged, burning about one million acres. GOES-18 monitored the spread of the fires and smoke across the region. The ABI instrument on GOES-18 observed the formation of pyrocumulonimbus clouds from intense fires in Alberta. The data collected by NOAA satellites help responders forecast what areas will be impacted and manage the wildfires. As the Northern Hemisphere heats up, NOAA satellites will keep watch for wildfires.
-
May 11, 2023: NOAA Awards Geostationary Ground System Sustainment Services Contract

Today, NOAA awarded the Geostationary Ground Sustainment Services (GGSS) contract to L3Harris Technologies Inc. of Palm Bay, Florida. The five-year Indefinite Delivery/Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) contract will provide sustainment services to extend the functions of the ground system that supports NOAA’s GOES-R Series. This contract provides for an indefinite quantity of supplies and services during the contract ordering period from May 11, 2023, through May 10, 2028. Individual supplies and service requirements will be defined at the task order level. The maximum value of this IDIQ contract is $275,169,157. The work will be performed at NOAA facilities located in Suitland, Maryland; College Park, Maryland; Wallops Island, Virginia; and Fairmont, West Virginia; and at the L3Harris facility in Melbourne, Florida.
-
May 4, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Preparing for Hurricane Season

As spring heads toward summer, NOAA satellites are ready for this year’s upcoming hurricane season. NOAA satellites monitor the conditions that spawn hurricanes and provide early warning that a storm is forming. GOES East and West monitor hurricanes as they develop and track their movements in near real-time. GOES satellites measure the temperature of cloud tops and the amount of water vapor present within a system, and also provide wind estimates. They also monitor lightning within a storm. NOAA satellites also aid emergency response to landfalling hurricanes by mapping the extent, damage and duration of flood events. Together, NOAA satellites are prepared to provide vital information to forecasters and help protect life and property throughout the 2023 hurricane season and beyond.
-
May 3, 2023: GOES-U Completes Solar Array Deployment Test
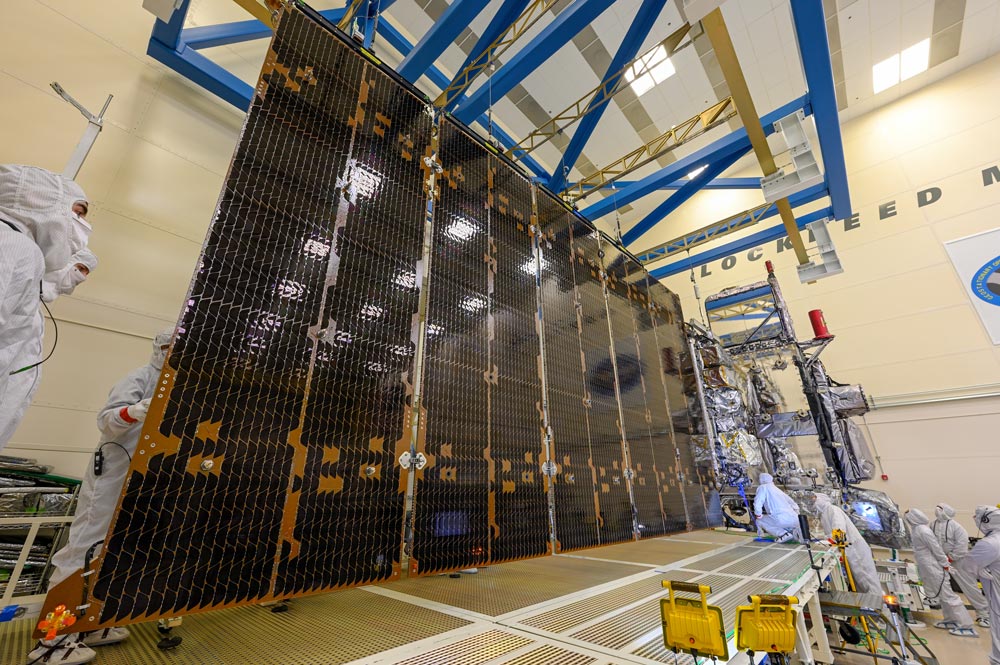

The GOES-U solar array fully deployed. Photo credit: Lockheed Martin GOES-U, the fourth and final satellite in NOAA’s GOES-R Series, recently completed a successful test deployment of its solar array to ensure it will function properly in space. This critical test verified that the satellite's large, five-panel solar array — which is folded up when the satellite is launched — will properly deploy when GOES-U reaches geostationary orbit. GOES-U’s solar array will convert energy from the sun into electricity to power the entire satellite, including the instruments, computers, data processors, sensors, and telecommunications equipment. GOES-U is scheduled to launch in 2024.
May
-
April 28, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Large Geomagnetic Storm Hits Earth

On April 21, 2023, NOAA satellites detected a coronal mass ejection erupting from the sun, which hurled plasma at two million miles per hour toward Earth. This eruption produced a geomagnetic storm on Earth. GOES-16’s Solar Ultraviolet Imager (SUVI) instrument observed the event as it occurred, while the DSCOVR satellite measured the solar winds the storm produced. This allowed NOAA to issue warnings for possible impacts from the storm. Geomagnetic storms can affect electrical grids, spacecraft, radio frequencies, GPS signals, and astronauts in space. On April 23, the particles reached Earth’s upper atmosphere and caused an aurora in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. This is the third severe geomagnetic storm since Solar Cycle 25 began in 2019. As the sun’s activity continues to ramp up, NOAA satellites will be watching for hazardous space weather.
-
April 21, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Happy Earth Day 2023

Since 1970, NOAA satellites have been monitoring Earth’s weather, environment, oceans, and climate. This Earth Day, we have a lot to celebrate. Over the past year, NOAA has added two new satellites to its Earth-observing fleet and contributed an instrument to a mission that will help us have a better understanding of Earth’s physical and biological environment. On Earth Day, we celebrate the critical information NOAA satellites provide to help us stay safe and the beautiful imagery they share of our planet. They see it all: hurricanes, severe thunderstorms, lightning, fires, dust storms, smoke, fog, volcanic eruptions, vegetation, snow and ice cover, flooding, sea and land surface temperature, ocean health and more. They can even track ship traffic and power outages. At NOAA, each day is Earth Day.
-
April 11, 2023: First Quarter 2023 GOES-R/GeoXO Newsletter

GOES-U acoustics testing. Photo credit: Lockheed Martin The GOES-R/GeoXO quarterly newsletter for January – March 2023 is now available. 2023 is off to an exciting start! We are just a little over a year away from the GOES-U launch, the final launch for the GOES-R Series. GOES-U completed mechanical environments testing and will next undergo electromagnetic interference/electromagnetic compatibility testing. We held our first GOES-R summit since 2019 and had the opportunity to collaborate in person with our colleagues from across the country. The newly operational GOES-18 satellite monitored a deluge of atmospheric rivers affecting the West Coast and an increasingly active sun. On GeoXO, we took our first step into implementation, with the award of the development contract for the imager, the primary instrument on our next-generation satellite system.
April
-
March 30, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Violent Storms Tear Through the South
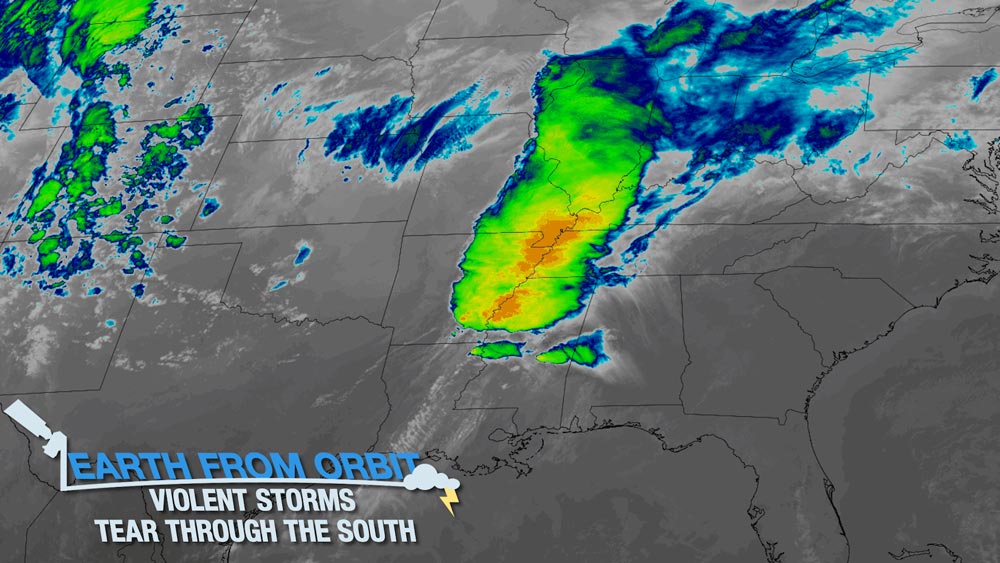
Beginning on March 24, 2023, NOAA satellites monitored severe storms that caused widespread damage from Texas to the Mid-Atlantic. The storms produced high winds, hail, flooding, and tornadoes. High winds and 38 tornadoes were reported when the storms moved through Mississippi, Alabama and Tennessee. The town of Rolling Fork, Mississippi was struck by an EF-4 tornado that killed 26 people in total, injured dozens more, and damaged buildings and utilities. GOES-16 (GOES East) monitored the storm in near real-time as it barreled across the Southeast.
-
March 24, 2023: Earth from Orbit: More Heavy Rain, Snow, and Wind Hitting Western U.S.
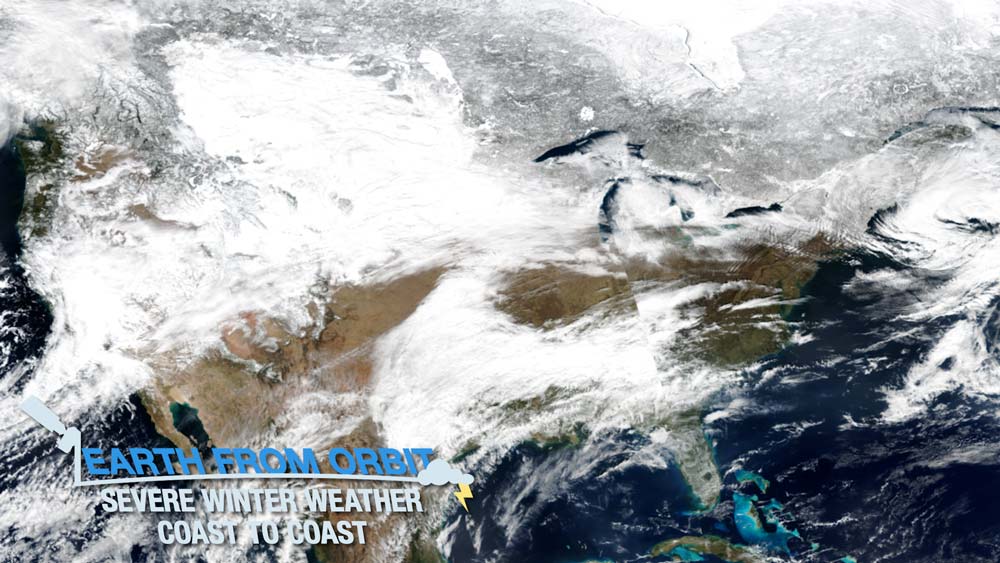

After tracking a series of atmospheric rivers that have drenched California this year, NOAA satellites monitored the latest storm to begin impact the state on Mar. 19, 2023. Rain and snow triggered flash flooding, caused numerous evacuations and left over 350,000 without power. The atmospheric river fueled a mid-latitude cyclone that led to the formation of a hurricane-like eye when two low pressure areas converged over San Francisco. NOAA satellites provided vital information about airborne moisture for more accurate weather forecasts and to predict flood risks and manage water resources.
-
March 2, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Monumental U.S. Storm Brings Severe Winter Weather Coast to Coast

Since mid-February 2023, winter weather has impacted the continental U.S. from California to Maine. In Southern California, the storm brought blizzard conditions to the San Bernardino and San Gabriel mountains as well as heavy rainfall to lower elevations. As the storm system continued eastward, snow and driving winds caused road closures and drifting snow across the Plains. Further south in Kansas and Oklahoma, tornadoes downed power lines, damaged property, and caused injuries. Additional tornadoes were reported in central and northeastern Illinois. The storm also brought heavy snow to the Northeast. NOAA satellites provided complementary measurements for a complete picture of this monumental storm and played a crucial role in tracking the storms across the U.S., alerting those in harm’s way.
March
-
Feb. 21, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Tropical Cyclone Freddy Breaks Records before Lashing Madagascar

On Feb. 21, 2023, Tropical Cyclone Freddy made landfall on Madagascar. Freddy formed on Feb. 5 near Indonesia and trekked more than 4,000 miles before hitting Madagascar. Freddy is one of only four storms on record to cross the Indian Ocean from east to west. It is also the first in the Southern Hemisphere to undergo four separate rounds of rapid intensification. At its strongest, Freddy had maximum sustained winds of more than 160 miles per hour, equivalent to a Category 5 hurricane. NOAA satellites and those from our international partners monitored the storm as it traversed the Indian Ocean and made landfall in Madagascar.
-
Feb. 9, 2023: Earth from Orbit: NOAA Satellites Track Blazing Wildfires in Chile

At least 231 wildfires have been blazing through south-central Chile since Feb. 3, 2023. The region is experiencing a “mega drought” with a decade-long period of dry weather. NOAA satellites are monitoring the fires as hot and dry weather persists. As of Feb. 8, 231 fires have burned more than 741,315 acres of land, making it the second worst year for acreage burned in Chile. GOES-16 and GOES-18 observed the movement of smoke from the fires in near-real time, while identifying new fires. The satellites also help determine a fire’s size and temperature. NOAA-20 and Suomi NPP provide detailed information on fire conditions. The satellites can detect smaller and lower-temperature fires and track wildfires in remote regions. Together, NOAA satellites provide critical and timely information used by fire crews, first responders and air traffic controllers.
-
Feb. 6, 2023: Keep Love in Your Orbit with NESDIS-Themed Valentine's Day Cards

We’re spreading the love again this Valentine's Day with a new collection of satellite-themed holiday cards. Circulate and celebrate with us by sharing these cards with your Earth-bound sweetie! The sentiment GOES a long way. Download the Valentines.
-
Feb. 2, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Rope Clouds
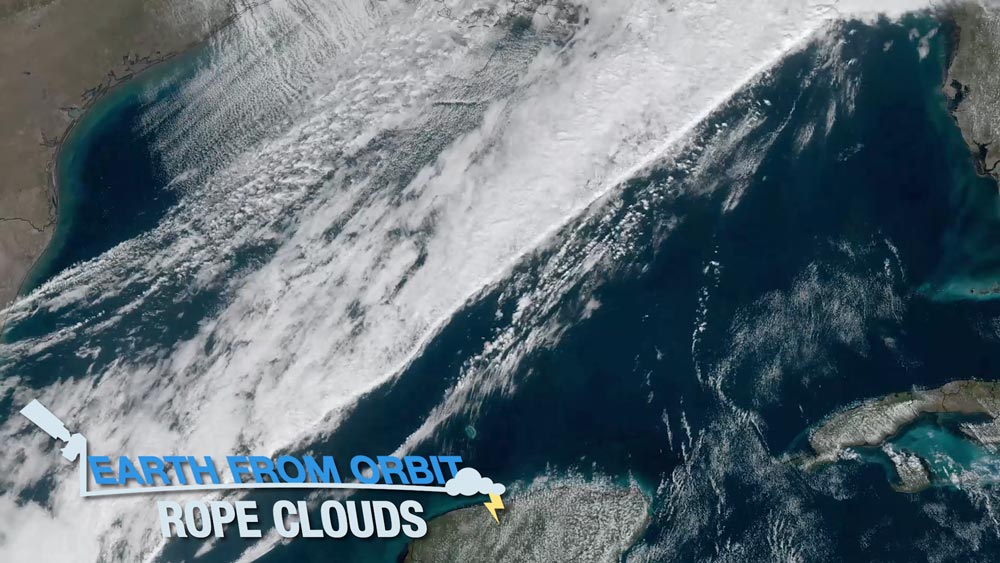
On Jan. 25, 2023, NOAA satellites captured an unusually long and long-lived rope cloud produced by a cold front over the Gulf of Mexico. A rope cloud is a very long, narrow, rope-like band of cumulus cloud formations. Generally associated with a cold front or a land-sea breeze front, rope clouds tend to form at the dividing line between cooler and warmer air. In this case, the rush of cool, dense air from the cold front pushed the warm, maritime air from the Gulf of Mexico upward, allowing water vapor to condense and the cloud to form. Satellite imagery can capture rope clouds, indicating a potentially changing weather pattern.
February
-
January 25, 2023: Earth from Orbit: Atmospheric Rivers Hit the West Coast
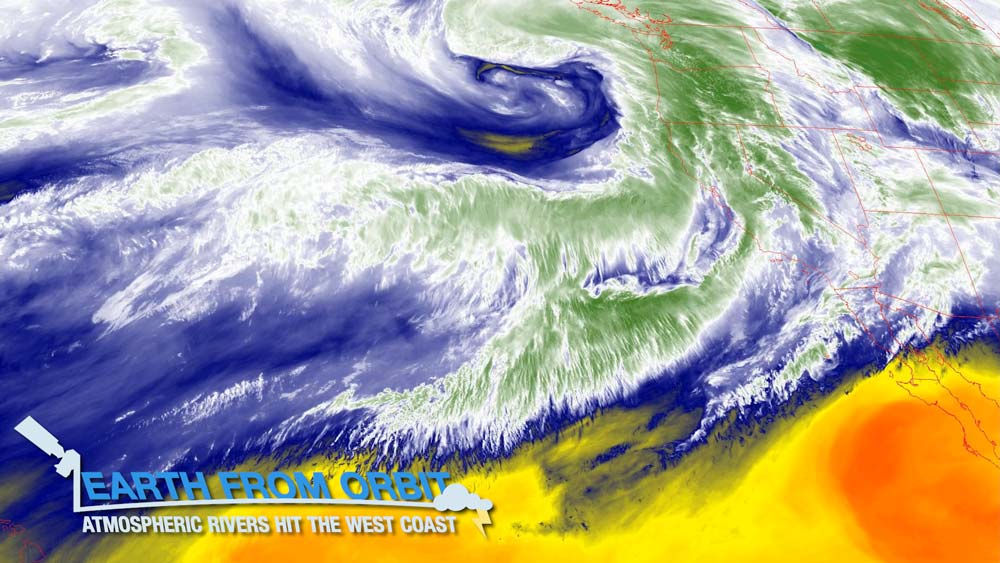
From late Dec. 2022 into Jan. 2023, a series of nine “atmospheric rivers” dumped a record amount of rain and mountain snow across the western U.S. and Canada, hitting California particularly hard. More than 32 trillion gallons of water rained down across the state, and the moisture also pushed into much of the Intermountain West. The San Francisco Bay area experienced its wettest three-week period in 161 years. Atmospheric rivers are long, narrow belts of moisture that move through the atmosphere. They can deliver tremendous amounts of rain, and high-elevation snow. This deluge of rain can provide relief for drought-stricken areas but also trigger flash flooding and mudslides. NOAA satellites help forecast these rivers in the sky and monitor the weather conditions they bring.
-
January 23, 2023: NOAA satellites helped save 397 lives in 2022
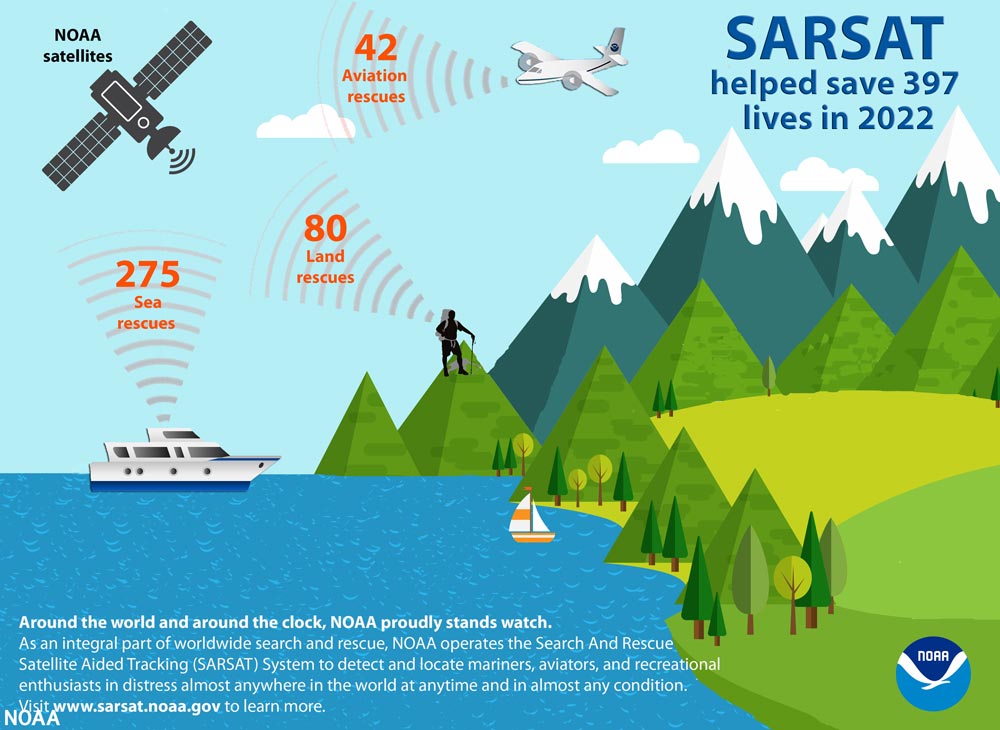
A graphic showing 3 categories of satellite-assisted rescues that took place in 2022: Of the 397 lives saved, 275 people were rescued at sea, 42 were rescued from aviation incidents and 80 were rescued from incidents on land. NOAA satellites, which are crucial in weather and climate forecasts, helped rescue 397 people from potentially life-threatening situations throughout the U.S. and its surrounding waters in 2022. NOAA’s polar-orbiting and geostationary satellites are part of the global Search and Rescue Satellite Aided Tracking system, or COSPAS-SARSAT, which uses a network of U.S. and international spacecraft to detect and locate distress signals sent from emergency beacons from aircraft, boats and handheld Personal Locator Beacons (PLBs) anywhere in the world. Of the 397 U.S. rescues last year, 275 were water rescues, 42 were from downed aircraft and 80 were on land involving PLBs. Florida had the most SARSAT rescues with 106, followed by Alaska with 56 and Utah with 20.
-
January 13, 2023: Fourth Quarter 2022 GOES-R/GeoXO Newsletter

RGB Developers Workshop participants. The GOES-R/GeoXO quarterly newsletter for October – December 2022 is now available. The GOES-R and GeoXO programs achieved new heights in 2022. We launched GOES-T, now known as GOES-18, completed on-orbit checkout, executed two GOES-17 and GOES-18 data interleave periods, and handed the satellite over to NOAA’s Office of Satellite and Product Operations. GOES-18 became NOAA’s operational GOES West satellite on Jan. 4, 2023. GOES-U is progressing toward its planned launch next spring, completing thermal vacuum testing and preparing for mechanical testing. And the future of NOAA’s geostationary satellite observations is assured, with the approval of the GeoXO Program.
-
January 04, 2023: NOAA’s GOES-18 is now GOES West

NOAA’s operational satellite fleet has a new member. GOES-18 entered service as GOES West on Jan. 4, 2023. The milestone comes after a Mar. 1, 2022, launch and post-launch testing of the satellite’s instruments, systems, and data. GOES-18 replaces GOES-17 as GOES West, located 22,236 miles above the equator over the Pacific Ocean. GOES-17 will become an on-orbit standby. In its new role, GOES-18 will serve as NOAA's primary geostationary satellite for detecting and monitoring Pacific hurricanes, atmospheric rivers, coastal fog, wildfires, volcanic eruptions, and other environmental phenomena that affect the western contiguous United States, Alaska, Hawaii, Mexico, and Central America. GOES-18 joins GOES-16 (GOES East) in operational service. Together the two satellites watch over more than half the globe, from the west coast of Africa to New Zealand and from near the Arctic Circle to the Antarctic Circle.